Setting up a strong computer network connection is key for today’s computing needs. It’s vital whether you work from home or just want to enjoy your favourite shows. A stable connection means better performance.
This guide looks at both wired Ethernet and wireless Wi-Fi setups. Each has its own benefits for different needs.
We’ll show you how to set up both Windows and macOS systems. Our expert advice will help you smoothly connect to your network.
A well-set network setup boosts your speed and security. Knowing both wired and wireless options helps you choose wisely.
The next parts will walk you through the wired and wireless setup steps. You’ll learn about cable connections and Wi-Fi settings.
Essential Network Components and Preparation
Building a reliable network starts with the right equipment and setup. Before you connect your computer, make sure you have everything you need. This step saves a lot of time later on.
Understanding Network Hardware Requirements
Modern networks need specific hardware to work well. You’ll need a broadband modem for internet and a wireless router to share it. These pieces form the base of your network.
Your computer also needs the right networking tools. Most devices have built-in adapters, but older ones might need extra. Knowing what you need ensures your network runs smoothly.
Gathering Necessary Equipment and Cables
Start by gathering all the network hardware you need. You’ll require a working broadband modem from your internet provider. Also, a good wireless router is key for your local network.
For wired connections, you’ll need Ethernet cables. Category 5e or Category 6 cables are best for homes and offices. Make sure you have cables long enough to reach your devices.
For wireless connections, you need compatible adapters. Most computers have these built-in, but check first. Having everything ready makes setting up your network much easier.
Network Configuration Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure your modem and router are on and connected. The modem must have an internet connection before adding more devices. This step is often missed but is very important.
Check if your computer sees its network hardware. Windows users can look in Device Manager under Network Adapters. macOS users can check in System Preferences under Network settings.
Have your network details ready, like SSID names and security keys. Having this info ready helps avoid problems during setup. Proper preparation makes setting up your network go smoothly.
How to Add a Computer to My Network via Ethernet Connection
Setting up a wired Ethernet connection gives you stable and reliable internet access. It avoids wireless interference and offers faster speeds. This method is great for desktops or fixed locations where cable management is easy.
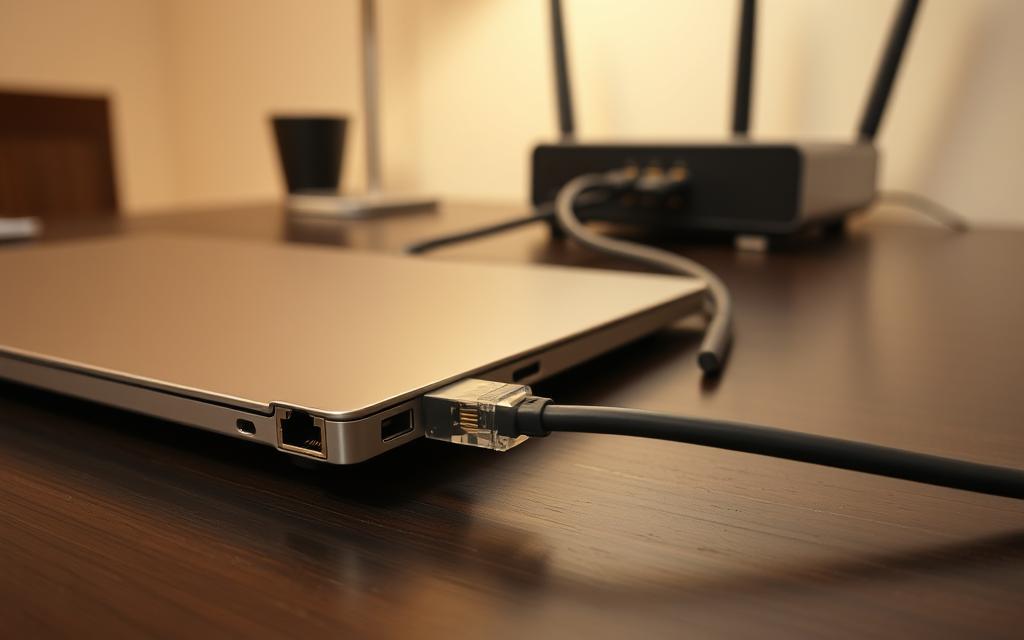

Physical Cable Connection Process
Start by getting an Ethernet cable. Cat5e or Cat6 cables work best. Make sure you have enough cable for the distance between your computer and router.
Find the LAN port on your computer. It’s usually on the back of desktops or sides of laptops. Then, find a LAN port on your router or modem. These ports are often colour-coded.
Plug one end of the Ethernet cable into your computer’s LAN port. You’ll hear a click. Then, plug the other end into your router’s port. Lights should turn on on both devices, showing it’s connected.
If your computer doesn’t have Ethernet ports, use a USB-to-Ethernet adapter. These small devices plug into your USB port and create a LAN connection.
Configuring Ethernet Settings in Windows
Windows usually sets up Ethernet connections automatically. To check, go to Network and Internet Settings in your Control Panel or system tray icon.
Here’s how to make sure everything is set up right:
- Open Settings and select Network & Internet
- Choose Ethernet from the left-hand menu
- Click on your Ethernet connection to view properties
- Make sure “IP assignment” is set to Automatic (DHCP)
- Also, ensure “DNS server assignment” is automatic
For most home networks, these settings will get you online right away. If you still have problems, you might need to update your network adapter drivers or router settings.
Configuring Ethernet Settings in macOS
Apple’s macOS makes setting up Ethernet connections easy. It usually recognises wired connections without needing manual setup.
To check or change your Ethernet settings on macOS:
- Open System Preferences and select Network
- Find Ethernet in the list of connection types
- Make sure it’s set to Using DHCP
- Check the status indicator shows Connected
- Look at the IP address assigned to your computer
Most users will find their Ethernet connection working right after plugging in the cable. Below is a table showing how Windows and macOS handle Ethernet settings differently:
| Configuration Aspect | Windows Approach | macOS Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Settings Location | Network & Internet Settings | System Preferences > Network |
| Automatic Detection | Usually immediate | Typically within seconds |
| Manual Configuration | Properties > Internet Protocol Version 4 | Advanced > TCP/IP |
| Status Indicators | System tray icon | Menu bar option (if enabled) |
| Troubleshooting Tools | Network Troubleshooter | Network Diagnostics |
Both Windows and macOS support Ethernet connections well. This makes setting up a wired network easy for users of either system. The physical connection is the same for both.
Establishing Wireless Network Connections
Connecting to a wireless network gives you freedom and flexibility. It’s better than wired connections. This guide helps you set up reliable wireless connections on different operating systems.
Locating and Selecting Your Wi-Fi Network
First, make sure your device’s wireless adapter is turned on. Most laptops have a switch or key combo for Wi-Fi. Once on, your device will look for nearby networks.
The network list shows all networks around you. Each network has its own name, or SSID. Pick the one you want to connect to carefully.
To find your network faster, move closer to the router if needed. Signal strength indicators help you choose the best connection.
Windows Wireless Configuration Steps
Windows makes setting up Wi-Fi easy. Look for the network icon in your system tray. It’s in the bottom-right corner of your screen. Clicking it shows available networks.
Here’s how to set up Windows Wi-Fi:
- Click the network icon in your taskbar
- Select your desired network from the list
- Check the “Connect automatically” option for future convenience
- Click the Connect button when prompted
- Enter your network security key when requested
Windows will try to connect to your network after you enter your key. If it works, you’ll see “Connected” under your network name.
macOS Wireless Connection Setup
Apple’s macOS is also easy to use for wireless connections. Start by clicking the Wi-Fi icon in your menu bar. It shows networks nearby.
Follow these steps for macOS Wi-Fi:
- Click the Wi-Fi icon in the top menu bar
- Choose your network from the dropdown list
- Enter the network password when prompted
- Optionally select “Remember this network” for automatic future connections
- Click Join to finalise the connection process
macOS will check your credentials and connect. The Wi-Fi icon in your menu bar will show signal strength once connected.
Both systems let you manage networks and troubleshoot problems. Remember, you need the right security key for your first connection.
Network Security and Authentication
Setting up a network is just the start. You need strong security to keep your digital space safe from hackers. It’s important to know about network security, set up authentication right, and stay alert to new cyber dangers.

Understanding Wireless Security Protocols
Today’s networks use wireless protocols to keep data safe. These standards have gotten better over time. But, WEP is old and not safe anymore.
WPA2 was a big step up, but WPA3 is the latest and best. It adds extra encryption and protects against hacking attempts. WPA3 also encrypts your connection on public networks, adding more security.
When setting up your router, pick the latest protocol. Most devices can still work with older ones, but newer ones get better security. Moving from WEP to WPA3 shows how wireless security keeps getting better.
Entering Network Security Keys
The security key is like a digital password for your network. You’ll need it when you connect devices. Modern systems hide what you type for privacy, so pay close attention.
Here’s how to keep your security key safe:
- Make strong passwords with letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Use a password manager or encrypted files to store keys.
- Avoid easy-to-guess passwords.
- Change your key often, especially in work settings.
Some routers have WPS for easy setup. But, it’s not always safe. Turn off WPS after you’ve set up your network to stay secure.
Enterprise Network Authentication
Big companies use special authentication methods for their networks. These systems control who gets in and what they can do. The 802.1X standard is often used for this.
These systems include:
- Unique user names and passwords instead of shared keys.
- Linking with directory services like Active Directory.
- Using certificates for extra security.
- Setting time limits and rules for access.
While home users use shared keys, knowing about these systems is good for small business owners. These systems offer better security and control. But, they can be complex and need IT help to set up.
Security is key, no matter how big your network is. Keep your security up to date and check it often. This way, you avoid problems and save time and money.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Network connections can sometimes fail, even with proper setup. Knowing how to diagnose and solve these problems saves time and reduces frustration. This section offers practical solutions for common network troubleshooting scenarios.
Ethernet Connection Problems
Start with physical checks when facing Ethernet issues. Ensure both ends of your cable are securely plugged in. Look for any visible damage to the cable itself.
Check if your network adapter is working right. In Windows, open Device Manager to see if there are warning symbols next to your network adapter. Try disabling and re-enabling the adapter to refresh the connection.
Test different LAN ports on your router if you have them. Some routers have specific ports for internet, while others serve multiple devices equally.
Wireless Connectivity Challenges
Wi-Fi problems often come from signal interference or setup errors. First, make sure your device’s wireless capability is enabled. Many laptops have physical switches or function key combinations for this.
Double-check you’re entering the correct security key. Wireless passwords are case-sensitive, so verify capitalisation matches your router settings exactly.
Signal strength greatly affects performance. If speeds are slow or you’re getting connection errors, try moving closer to your router or removing physical obstructions. For persistent Wi-Fi problems, restart both your computer and wireless router.
Router and Modem Configuration Checks
Proper router configuration is key for reliable networking. Start by checking if both router and modem have power and show normal lights. Most devices display specific patterns for internet status.
Look for firmware updates through your router’s administration interface. Manufacturers often release updates to improve stability and security.
If issues persist across devices, consider a router reset. This will restore factory settings, requiring you to reconfigure your network preferences afterwards.
For modem-related problems, contact your internet service provider. They can remotely check connection quality and signal levels to find external issues affecting your service.
Conclusion
Both wired Ethernet and wireless Wi-Fi are good ways to connect your computer. Ethernet is fast and reliable for staying in one place. Wi-Fi is great for moving around with laptops and mobile devices. Your choice depends on what you need and how you use your devices.
Security is key, no matter how you connect. Use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption for Wi-Fi and strong, unique passwords. In big places, use the right ways to check who can get in and keep data safe.
To keep your network running well, check cables, update router software, and watch your Wi-Fi signal. Fixing problems early stops them from messing up your work.
Choose between Ethernet’s stability and Wi-Fi’s ease based on what you need. Make sure each device on your network has the best connection for it.
FAQ
What are the main benefits of using a wired Ethernet connection versus a wireless one?
A wired Ethernet connection is more stable and faster than wireless. It’s less likely to be affected by interference. This makes it great for activities like gaming, streaming, or transferring large files.
Wireless connections, however, offer more freedom. You can connect from anywhere without cables. This is perfect for those who need to move around.
What hardware is essential for setting up a network connection?
You’ll need a broadband modem, a wireless router, and a network adapter. For wired connections, an Ethernet cable is also necessary. Make sure your modem and router are connected and turned on before adding a device.
How can I check if my computer has a built-in wireless adapter?
On a Windows computer, open Device Manager by right-clicking the Start button. Look for “Wi-Fi” or “Wireless” under “Network adapters”.
On a macOS device, go to System Preferences > Network. If Wi-Fi is listed, your device has a wireless adapter.
What type of Ethernet cable should I use for a wired connection?
For home and office networks, a Cat 5e or Cat 6 Ethernet cable is best. They support speeds up to 1 Gbps and work well with modern devices. Make sure the cable is in good condition and the right length.
How do I connect my computer to the network using an Ethernet cable?
Plug one end of the Ethernet cable into your router or modem. Then, plug the other end into your computer’s Ethernet port. Most systems will automatically set up the connection.
If not, check your network settings. Make sure DHCP is enabled.
What steps should I follow to connect to a wireless network on Windows?
Click the network icon in the taskbar. Select your Wi-Fi network from the list. Enter the security key and click “Connect”. Make sure Wi-Fi is turned on first.
How do I connect to a Wi-Fi network on a macOS device?
Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar. Choose your network from the list. Enter the password and click “Join”. If you can’t see the network, check you’re in range and Wi-Fi is on in System Preferences > Network.
What is the most secure wireless security protocol to use?
WPA3 is the most secure protocol, offering strong protection against hackers. If your router only supports WPA2, it’s still a good choice. Avoid WEP as it’s outdated and not secure.
What should I do if my computer does not detect any wireless networks?
First, check if Wi-Fi is turned on. If it is, try moving closer to the router. Restarting your router or computer might help.
If the problem continues, check your device’s network adapter drivers or settings.
How can I troubleshoot an Ethernet connection that is not working?
Make sure the Ethernet cable is securely plugged into both the router and your computer. Check the router’s LAN port lights are on. Test the cable and port with another device if you can.
Also, ensure your network adapter is working right through Device Manager (Windows) or Network Preferences (macOS).
What are the common reasons for a slow or unstable wireless connection?
Common issues include being too far from the router, physical barriers, and interference from other devices. Try moving your router, reducing interference, and keeping your equipment updated.
How important is it to keep my network security key safe?
Keeping your network security key secret is very important. It prevents unwanted access to your network. Don’t share it with anyone and change it regularly for extra security. For business networks, there are more security steps, but at home, the key is your main defence.