Every efficient digital setup starts with a well-thought-out connection plan. This plan shapes how data moves between devices and systems.
Network topology is about both physical links and data paths. These designs impact performance, security, and how well a network can grow.
Today’s systems are made up of connected nodes like routers, switches, and devices for users. These connections are key to digital communication.
Knowing about different network topologies is key for designing networks well. The way links and nodes are arranged affects how data is sent.
Both the physical setup and data flow are crucial in planning networks. This helps experts build strong, flexible digital spaces.
Understanding What is a Computer Network Topology
Network topology is like a blueprint for how devices talk to each other online. It shows how things are set up physically and how data moves. Knowing this is key to making networks work well and fixing problems.
Defining Network Topology and Its Role
Physical topology is about the real setup of network parts and how they’re connected. It’s about where devices are and the cables that link them. This setup affects costs, upkeep, and how big the network can grow.
Logical topology is about how data moves, not where the cables are. It’s about the rules for data flow and how signals are sent. Even if a network looks like a star, its data flow might be like a ring.
It’s important to know the difference between physical and logical topology. Physical deals with where things are and cables. Logical is about data paths and rules. Both must work together for the network to perform well.
Key Components in Topology Designs
Every network has two main parts: network nodes and links. Nodes are where data packets go in or out. These can be computers, servers, or even IoT devices. Each node has its own address.
Links are the paths that connect nodes. They can be cables or wireless signals. The type of link affects how fast data moves and how reliable the network is.
Think of an office network: computers (nodes) are connected to a switch (node) with Ethernet cables (links). The switch then links to routers (nodes) via fibre optic cables (links) to the internet. This setup lets everyone in the office communicate.
Bus Topology Layout and Its Characteristics
Bus topology is known for its simple design, using a shared backbone cable. It connects all devices to one channel, making data transmission easy. This design is still useful in small setups where keeping costs low is key.
Overview of the Bus Topology Structure
The bus topology has a central cable, often coaxial or twisted pair, as its backbone. Devices like computers and printers connect to this cable. Data moves in both directions, with each device knowing its packets.
This setup looks like a straight line with devices at different points. Termination resistors at both ends stop signal reflections, keeping data clear.

Advantages of Using Bus Topology
Bus networks are simple and cost-effective. They need less cabling since devices connect to the main cable. This makes installation easy.
Other benefits include:
- Easy to add more devices
- Less cable than star setups
- Easy to find problems by isolating segments
- Good for small networks
Bus topology is great for temporary setups or small offices. It’s perfect when you’re on a tight budget but need basic connectivity.
Disadvantages and Limitations of Bus Topology
Bus topology has big downsides. The main issue is the single point of failure. Damage to the backbone cable can shut down the whole network.
As more devices join, the shared medium causes problems. Data collisions happen when devices try to send data at the same time. This slows down the network.
Security is also a worry. Since all devices share the same medium, data can be intercepted. This is a big problem in places where keeping data safe is crucial.
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage | Impact Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cable Requirements | Minimal length needed | Single cable failure disrupts entire network | High |
| Performance | Adequate for light traffic | Data collisions increase with more devices | Medium-High |
| Security | Simple configuration | All transmissions are broadcast on shared medium | High |
| Cost | Low implementation expense | Potential downtime costs from failures | Variable |
| Scalability | Easy to add devices | Performance decreases with expansion | Medium |
Early Ethernet networks used bus topology. Today, we prefer stronger designs. But, knowing bus topology is still important for working with old systems or specific needs.
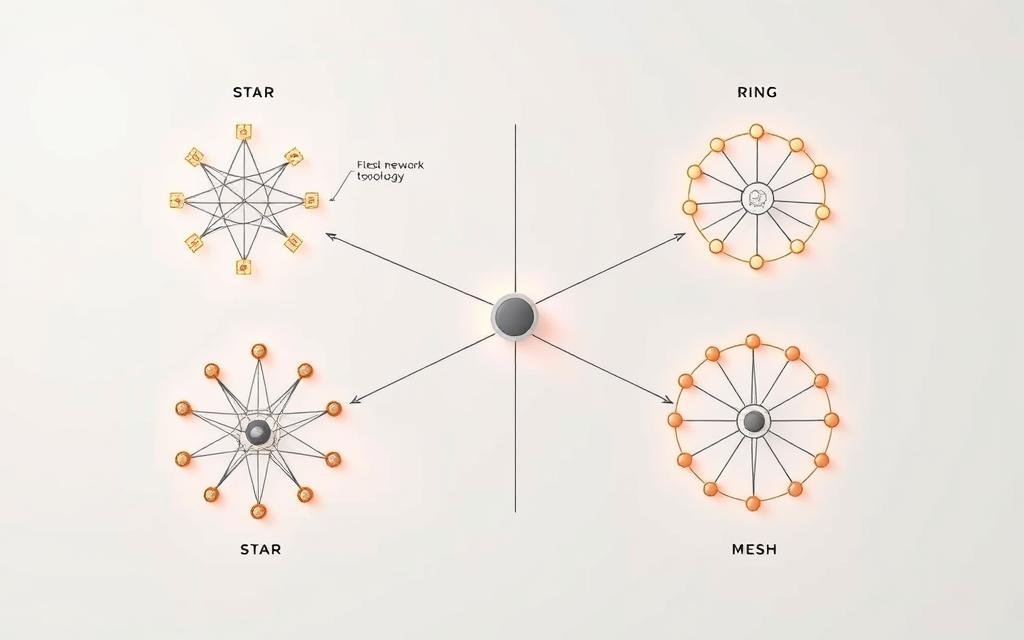
Star Topology Design and Functionality
Star topology is a key network setup known for its organised layout. It’s widely used in today’s networks. All devices connect to a central point, making it efficient and easy to manage.
How Star Topology Operates
In a star network, each device links directly to a central hub or switch. This hub is the network’s core, handling all data exchanges. The setup looks like a star, with the hub at the centre and devices spreading out.
Data moves from devices to the hub, then to its destination. This central control makes managing data easy and ensures smooth communication. It also makes monitoring and managing network traffic straightforward.
Benefits of Star Topology in Networks
Star networks have many benefits. One major plus is fault isolation. If a device fails, it doesn’t bring down the whole network. This makes troubleshooting easier.
Other star network advantages include:
- Easy setup and adding new devices
- Simple management through the central hub
- Improved security with centralised monitoring
- Better performance than bus topology networks
The setup makes adding or removing devices simple. This flexibility is why it’s popular in offices and local networks.
Drawbacks of Star Topology
Star topology has some downsides. The biggest issue is its reliance on the central hub. If it fails, the network stops working. This is the main weakness.
Hub failure can happen for many reasons, like power outages or hardware problems. When the hub goes down, all devices lose connection. This makes careful planning essential.
Other issues include:
- Higher costs for cabling
- Space needed for the hub
- Hub capacity limits performance
- Network slowdown during busy times
| Aspect | Advantage | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Network Management | Centralised control makes administration easier | Needs skilled people for hub management |
| Cost Efficiency | Less time spent on troubleshooting | Higher initial cost |
| Reliability | Device failures don’t affect others | Network fails if hub has issues |
| Scalability | Easy to add new devices | Hub capacity limits growth |
| Performance | Consistent data speeds | Hub’s power affects performance |
Modern office LANs often use star topology with switches as the hub. Home Wi-Fi networks also use this setup, with routers as the central hub. These examples show how practical star topology is in real life.
Network admins need to consider these points when choosing star topology. It’s great for fault isolation and management but needs strong hub solutions to avoid hub failure risks.
Ring Topology: Structure and Operational Details
Ring topology is a unique way to connect devices in a circular path. This setup makes data travel in one direction, offering both benefits and challenges for network managers.
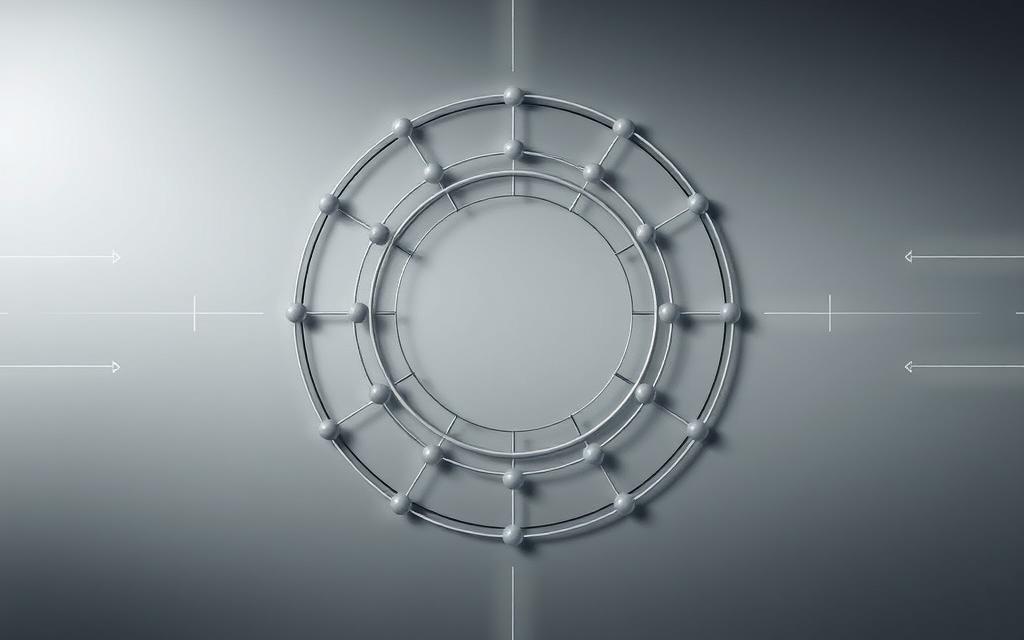

Explanation of Ring Topology Layout
In a ring topology, devices link up in a circle. Each device connects to two others, forming a continuous loop. Data moves in one direction, following the circle.
Network engineers use token passing to manage data. This method lets devices send data only when they have a special token. It stops data from getting mixed up and keeps communication smooth.
“Ring topology is one of the most organised network structures. Data moves in a set path, with little chance of problems.”
Advantages of Ring Topology
Ring networks are cost-effective and efficient. They are easy on the wallet and work well, making them great for budget-friendly setups. Data moves quickly and reliably.
The circular design gives everyone equal access. No single device can control the network. This makes ring topology good for fair communication.
| Advantage | Description | Practical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Lower installation and maintenance expenses | Small to medium business networks |
| Predictable Performance | Consistent data transmission speeds | Time-sensitive applications |
| Equal Network Access | Balanced resource distribution | Collaborative work environments |
| Easy Expansion | Simple addition of new nodes | Growing organisational needs |
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
The circular design has its downsides. A single device failure can stop the whole network. This is a big problem.
To fix this, some use a dual-ring network. This has two rings that send data in opposite directions. It helps the network keep working even if one ring fails.
Adding or removing devices also has its challenges. It often means shutting down the network. Finding and fixing problems can be hard because of the ring’s design.
Despite these issues, ring topology is still useful in certain situations. Knowing its pros and cons helps in making the right choice for network design.
Mesh Topology and Hybrid Designs
Mesh networks have lots of connections between devices for better reliability. They are great for companies that need strong, reliable networks.
Understanding Mesh Topology
Mesh topology is a complex network setup with many connections between nodes. It’s different from star or bus layouts because it has more paths for data. This makes the network more reliable.
Each device is connected directly to others, avoiding single points of failure. This is very useful in situations where keeping connected is crucial.
Full Mesh Topology Configuration
A full mesh setup connects every device directly. This means there are lots of connections, making the network very reliable.
Even if one connection fails, others can still keep the network running. The internet backbone is a good example of this.
Full mesh designs are used in places like the military and finance because they’re so reliable. The cost is high, but it’s worth it to avoid downtime.
Partial Mesh Topology Setup
Partial mesh is a mix of robustness and cost savings. Only key devices have many connections, while others connect through these nodes.
This makes it cheaper than full mesh but still keeps the network reliable. It’s a good choice for companies that need to save money but still want a strong network.
Many companies use partial mesh for a good balance. It’s not as expensive as full mesh but still offers enough reliability.
Hybrid Topology: Combining Layouts
Hybrid network designs mix different topologies. This lets network architects create custom solutions for their needs.
They might use star-bus or star-ring layouts to get the best of both worlds. Universities often use these custom hybrid network designs.
Designing a hybrid network needs careful planning. It’s about understanding the network’s needs and how it will be used.
Pros and Cons of Mesh and Hybrid Topologies
Mesh and hybrid topologies have their own benefits and drawbacks:
- Enhanced reliability through multiple paths
- Superior fault tolerance compared to simpler designs
- Scalability for growing networks
- Customisation options with hybrid designs
But, there are also challenges:
- Higher implementation cost for lots of cabling
- Increased complexity in setup and upkeep
- Network management challenges with many connections
- Design expertise required for best results
Companies need to think about these points when deciding on a network. It’s about whether the extra cost is worth it for better reliability.
Selecting the Appropriate Network Topology
Choosing the right network topology is crucial. It affects your organisation’s daily operations and future growth. You need to consider your specific needs and constraints.
Evaluating Network Requirements
Start by looking at your current and future network needs. Think about data volume, user numbers, and the types of applications you use. High-traffic areas need strong network performance.
How important is fault tolerance for your organisation? Critical systems need redundancy. Financial institutions often choose mesh designs for their reliability.
Think about your growth plans. Startups might look for cost-effective solutions. Large companies focus on scalability.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Different Topologies
Each network topology has its own financial aspects. The total cost of ownership includes setup, upkeep, and downtime costs.
Bus topology is cheap upfront but costs more over time. Star networks are more affordable and reliable. Mesh topologies are the most expensive but reduce downtime risks.
Here’s a comparison:
| Topology Type | Initial Cost | Maintenance Cost | Downtime Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bus | Low | Medium | High |
| Star | Medium | Low | Medium |
| Mesh | High | Low | Low |
Future-Proofing Your Network Design
Think about future tech and growth. Choose topologies that can handle new technologies like IoT and cloud integration.
Security considerations must keep up with your network. Centralised designs are easier to manage. Decentralised designs offer security through diverse paths.
Use modular designs for easy expansion. This saves money and supports future needs. Regular network checks ensure your design meets your organisation’s needs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right network topology is crucial for any organisation. It greatly affects performance, reliability, and security. A good layout helps data flow smoothly and makes management easier.
This article covered the main types of topologies: bus, star, ring, mesh, and hybrid. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. Knowing these helps you pick the best one for your needs.
Following best practices in network design is key to a strong infrastructure. Regular upkeep, security, and planning for growth are vital. For more on this, check out this resource on network topology.
Think carefully about what you need. The right topology boosts efficiency and supports your business goals. It lays a solid base for your network’s success.
FAQ
What is the difference between physical and logical network topology?
Physical topology shows how devices and cables are laid out. It’s about where routers, switches, and computers are placed. Logical topology, however, is about how data moves between devices, no matter their physical setup. Both are key in planning a network.
Why is network topology important for performance and security?
Topology affects how well a network works by influencing data flow and potential bottlenecks. For security, some topologies, like mesh, are safer because they’re more redundant. Others, like bus, can be riskier because they share media. Picking the right topology balances these needs.
What are nodes and links in network topology?
Nodes are devices in a network, like computers and routers. Links are the connections between these nodes, which can be cables or wireless channels. Together, they form the base of any network design.
What are the main advantages and disadvantages of bus topology?
Bus topology is cheap and easy to set up, great for small networks. But, it has big downsides: it’s vulnerable to a single failure, and data collisions increase as more devices join. This makes it less reliable for larger networks.
How does star topology improve fault isolation in networks?
In star topology, each device connects to a central hub. If one device fails, it doesn’t affect others. This makes fixing problems easier, but the network’s success depends on the hub’s reliability.
What is token passing in ring topology, and how does it work?
Token passing is a method in ring topology where a special signal, the token, goes around the network. Only the device with the token can send data, preventing collisions. It ensures smooth data flow but can fail if a node breaks.
When should mesh topology be used over other types?
Mesh topology, especially full mesh, is best for high-reliability needs like internet backbones or financial systems. It offers strong security and performance but is expensive and complex. It’s not for small setups.
What factors should be considered when selecting a network topology?
Consider performance, reliability, scalability, budget, and security. Think about data volume, growth, and downtime tolerance. This helps choose a topology that meets your needs, like bus for small setups or mesh for critical systems.
How can hybrid topology benefit large organisations?
Hybrid topology mixes different topologies, like star-bus or star-ring, for custom solutions. It supports complex, scalable networks in universities or big companies. But, it needs careful design and more maintenance.
What role does future-proofing play in network topology selection?
Future-proofing means designing a network that can grow with new technologies without big changes. Choosing a scalable topology and planning for upgrades ensures the network stays efficient and relevant over time.